Machine Learning 101
Machines are good at certain things like computers can perform certain task at a really fast pace. We can program computers to do those tasks. For example if we want to go to someone’s house we have to option -
- Take a map and a ruler and map out all the routes from my current location to destination and find the shortest path to take.
- You can ask computer to tell me how to get to my destination, through programming.
Instead of working 10 mins myself to calculate all possible routes, I can simply press a button and computer will tell me the shortest route. Companies saved a lot of money by using computers as they dont have to hire a ton of workers and computers can do their task instead. But these machines are only good on the task which we can program by using if else programs. For example if we go ahead and program the above code it will look something like this :
if : route 1 < route 2
if : route 1 < route 3
if : route 1 < route 4
if : route 1 < route 5
then : pick route 1
Computers are very good at performing task which have set defined rules. Now let’s consider another example. We want our machine to detect a person emotion by reading the review he/she posted for a product on Amazon. Now using an if else block we cant describe to a computer what angry means. The harder the things become to describe the harder it is for us to tell machines what to do. So we hire humans to do this tough part and let computers handle the easy part. The things which computers were not be able to do before and only humans could do can now be done by machines with machine learning. The goal of machine learning is to make machine act more and more like humans.
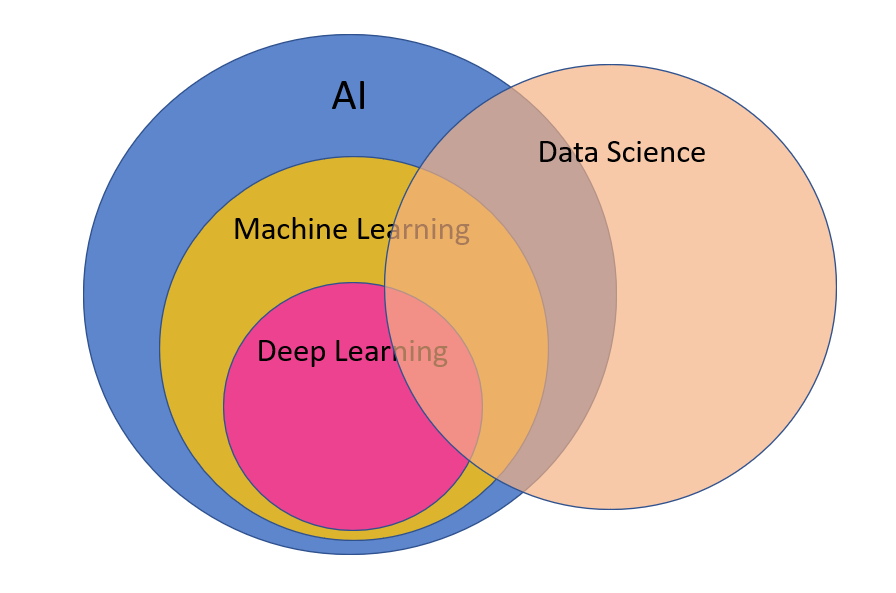
It all starts with AI or artificial intelligence which means human intelligence demonstrated by machines. We also have Narrow AI which means where machines are just as good or even better then humans at some tasks. Each AI is only good at one task. Narrow AI is good at just one task, they dont have multiple abilities like humans. Machine Learning is a subset of AI. ML is an approach to reach AI through systems that can find patterns in a set of data.
Stanford ML Definition - Science of getting the computers to act without being explicitly programmed that is getting machines to do things without us specifically saying if this than that.
Deep Learning is just one of the techniques for implementing machine learning.
The field of data science simply means analyzing data looking at data and then doing something with that data. Data Science and Machine Learning are overlapping things. You cant do one without the other.
Teachable Machine
There is an online project developed by Google - Teachable Machine
On this website you can play with some interesting machine learning projects. A Basic one is that you provide machine some images pre-classified in respective groups. The website will analyze them and train a ML model based on the input. After the model is created when ever you will provide a new image the model will try to classify the image into a group.
And that’s how exactly a ML machine works. You provide some inputs to the machine. Then you tell it what type of data it is. The machine will learn automatically based on inputs and will give corresponding output whenever you will ask any question to it. After testing the above website you will come to know that it is not accurate because to train a ML model you require thousands and millions of data. The more data you will provide to the machine the better it can predict the output.
Why Machine Learning
Everything that we learn there should be a reason we’re learning it right. And you might be asking yourself why do we even care about machine learning how is that useful and how do we get here. Well if you think about a business because most technology evolves from business needs we have the advent of computers and the ability for businesses to use computers to do things really really fast and efficiently so that they gain an edge. Previously this data was stored in spreadsheets which was very easy to read from a human perspective. We started getting more and more information and data and we needed a better way to organize things to understand things from our data. Maybe if you were Amazon you can use customers purchasing history to recommend different products. And ever since then this idea of data getting more and more data has turned us into using machine learning because at some point we have so much data that as humans we can’t just look like we did at spreadsheets and look at columns and rows and make business decisions I mean we still could but then we’d be wasting all this data that we’ve been getting over the years. So using the massive amounts of data and massive improvements in computation we can use these machines to give them this big data and make a decision for us just like we used to with spreadsheets.
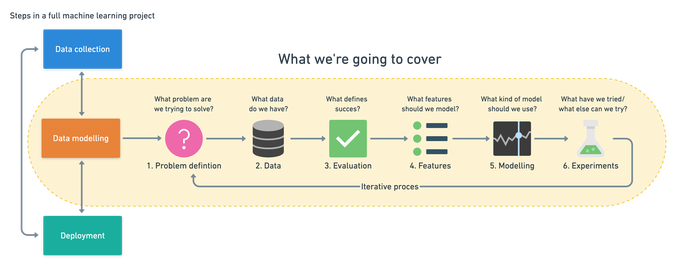
We need to understand what data is and then apply machine learning to it. And the industry is now evolving into these people that want to be data scientists that is people that can turn data from use less to use for.
Machine Learning Playground
There is an online project - ML Playground
Here you can directly input your data sets, select on which ML algorithm you want to run the data on and viola you will get a ready made model. Go ahead and play around with it a little bit.
Types of Machine Learning
-
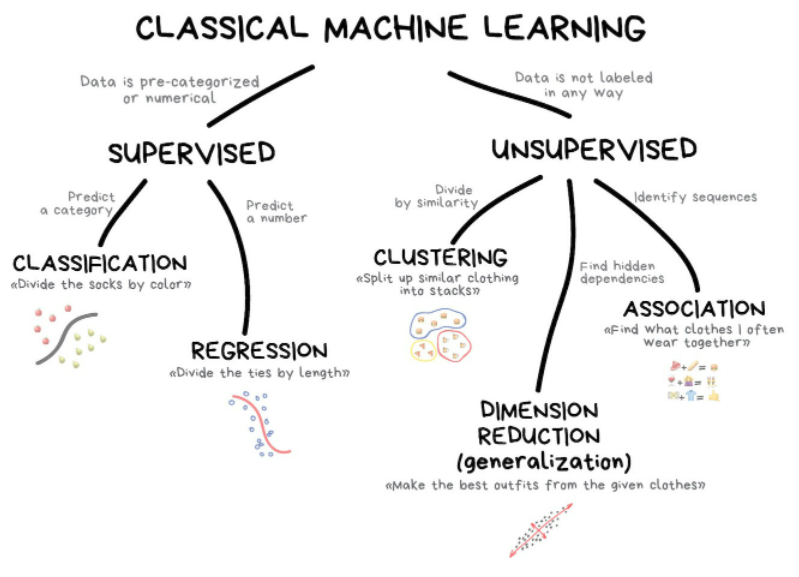
Supervised Learning - In this the data that we received already has categories. Think of it as a CSV files with rows and columns label. We have labeled data and a test data that is label so we know if our function is right or wrong. So in a supervised learning scenario, we can do things like classification to decide is this an apple or is this a pear. Or we might do something called regression instead of classification based on inputs, for example, predicting stock prices.
-
Unsupervised Learning - Now, sometimes we have data that doesn’t have labels and this is called unsupervised learning. Again, think of it as a CSV file without the column names label. Sometimes with things like clustering. We need to create these groups or at least the machine to create these groups. For example, we give it a bunch of data points and then the machine decides, oh, this is a group, this is a group and this is a group. Or we can have something like Association Rule Learning where we associate different things to predict what a customer perhaps might buy in the future. When groups don’t exist, we call it unsupervised learning.
-
Reinforcement Learning - Reinforcement learning is really interesting because it’s all about teaching machines through trial and error, through rewards and punishment. So the program simply learns a game by playing it millions of times until, well, it gets the highest score, it doesn’t know what it’s doing at first, but then it tries to maximize the score and eventually figures out that, hey, maybe I should try and move where the ball is coming. So this is scene for skill acquisition or real time learning. And you see it a lot in machine learning programs that play, for example, video games.
Machine Learning in a Nutshell
Machine learning is using an algorithm or computer program to learn about different patterns in data and then taking that algorithm and what it’s learned to make predictions about the future using similar data. Machine learning algorithms are also called models. How machine learning algorithms differ from normal algorithms and computer programs is the learning aspect.
Let’s use an example where a normal algorithm could be a set of instructions, such as how to turn a pile of raw ingredients into your favorite honey mustard chicken dish. The set of instructions might start out by saying, first, cut up the vegetables, then season the chicken, then preheat the oven, etc. And if you follow these steps correctly, you’ll end up with your favorite honey mustard chicken dish. What’s important to note here is you start with an input, your set of ingredients and a set of instructions on what to do to get to your favorite dish.
What happens with a machine learning algorithm is instead of starting with an input and a set of instructions, you start with an input, an ideal output. In our case, the ingredients is the input and the output is our favorite chicken dish. And what a machine learning algorithm does is it looks at the input, the raw ingredients, and then it looks at the output, the favorite chicken dish, and it tries to figure out the set of instructions in between these two.
Now, think about this, if you tried to do this on your first try, you might not get great results. You might put in too much spice in the dishes, come out far too hot when you second trying to get a little closer. If you looked at the set of ingredients and ideal outputs, your favorite chicken dish hundred plus times, you’d probably get pretty good or pretty close to figuring out what the set of instructions are to make that dish.
Now, we’re missing out a few steps here, but this is what machine models do in a nutshell. They find patterns collected in data so we can use those patterns for future problems.